What is Induction Cooking?
Induction cooking uses electromagnetic energy to heat your pots and pans directly. When compatible cookware is placed on the smooth glass cooktop, a magnetic field activates, generating heat through friction. Instead of heating the surface, the cookware itself becomes the heat source, ensuring fast, efficient, and precise cooking!
Read below to learn more about induction cooking, compare cooking methods, and check out our offers for RCEA customers! You can even try induction for FREE!
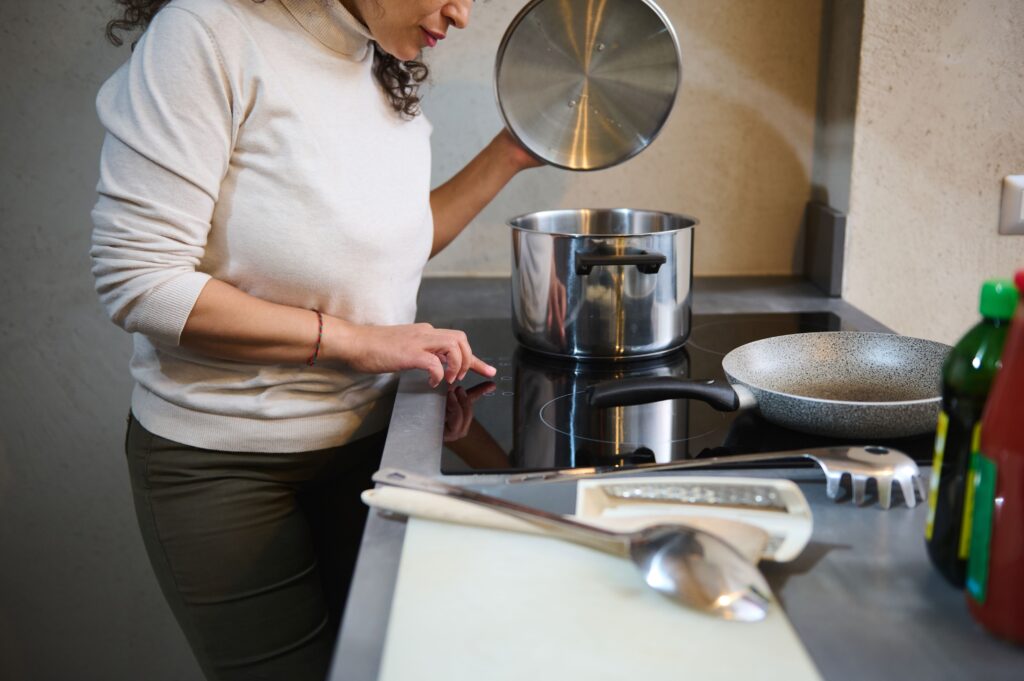

Benefits of Induction Cooking
- Energy Efficiency – Uses less energy by heating cookware directly, reducing wasted heat.
- Faster Cooking – Boils water and cooks food quicker than gas or electric coil stoves.
- Precise Temperature Control – Provides instant adjustments for better cooking accuracy.
- Safety – The cooktop stays cool to the touch, reducing the risk of burns or fire hazards.
- Easy Cleanup – Smooth glass surface that doesn’t heat up itself means spills don’t burn, making cleanup simple.
- Better Indoor Air Quality – Produces no harmful pollutants, improving air quality in your home.
How Does Induction Compare?

Efficiency
How much heat reaches your food
Induction
- Up to 90% efficient
- Keeps kitchen cool by not wasting heat
Electric Coils
- About 74% efficient
Natural Gas
- About 40% efficient
Safety
How safe the stove is to use
Induction
- No open flame
- Cooking surface stays cool to the touch
- No toxic emissions
Electric Coils
- Hot cooking surface poses a risk of burns or fire
- No toxic emissions
Natural Gas
- Open flame poses a risk of burns or fire
- Possible gas leaks are a health and safety hazard
- Emits toxic gases like nitrogen oxides, benzene, and methane
Cooking Experience
What it’s like to cook with the stove
Induction
- Rapid heating
- Instant temperature adjustments
- Temperature display (on some models)
- Precise temperature control
Electric Coils
- Slow to heat
- Slow temperature adjustments
- Less temperature control
Natural Gas
- Moderate heating speed
- Quick temperature adjustments
- Less temperature control
Cleaning Experience
What it’s like to clean the stove
Induction
- Cool surface means spills don’t burn on
- Smooth glass top means easy cleaning
- Harsh abrasives may scratch surface
Electric Coils
- Hot surface means burned-on and hard to remove spills
- Requires disassembly to clean
- Must be cleaned frequently for safety
Natural Gas
- Hot surface means burned-on and hard to remove spills
- Requires disassembly to clean
- Must be cleaned frequently for safety
Cost
Cost of purchase and installation
Induction
- Highest cost
- Money-saving rebates available
Electric Coils
- Lowest cost
- Money-saving rebates available if replacing natural gas
Natural Gas
- Moderate cost
- No rebates available from RCEA
Offers for RCEA Customers
Try it For Free
Curious about induction cooking? Try it for free with the Induction Cooktop Lending Program!
Save Money with Rebates
Check out our Kitchen Appliance Rebates page for rebates on induction cooktops and stoves. Get money back on your upgrade to cleaner cooking!


FAQs
Gas stoves, even with proper use and maintenance, emit small amounts of toxic gases into your home. The most common pollutants from gas stoves are nitrogen dioxide (NO2), carbon monoxide and formaldehyde. Advocates now are mostly focused on NO2, which the Environmental Protection Agency says is a toxic gas that even in low concentrations can trigger breathing problems for people with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (npr.org).
Any cookware with a ferromagnetic bottom is compatible with induction. Use a magnet to test your cookware for compatibility: if the magnet sticks, you’re good to go!
Yes, with careful use. Heavy pans could scratch or crack the glass surface if dropped.